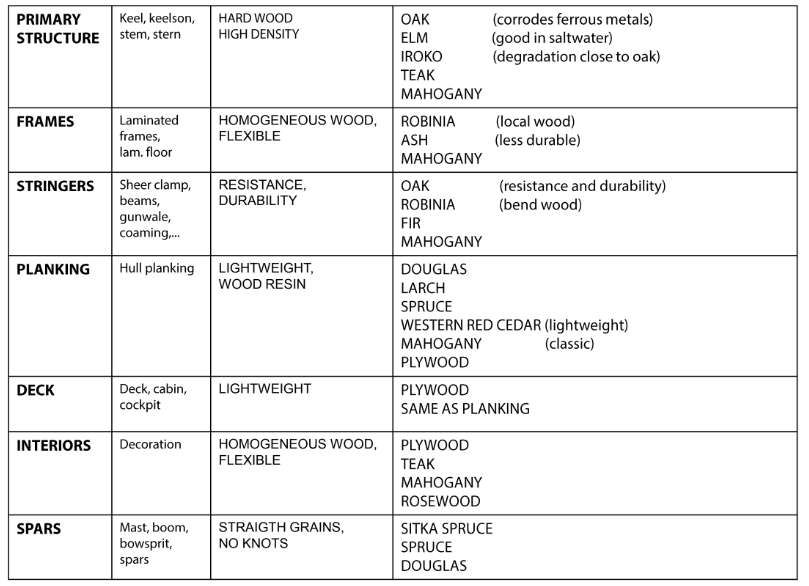
Tecniche di costruzione
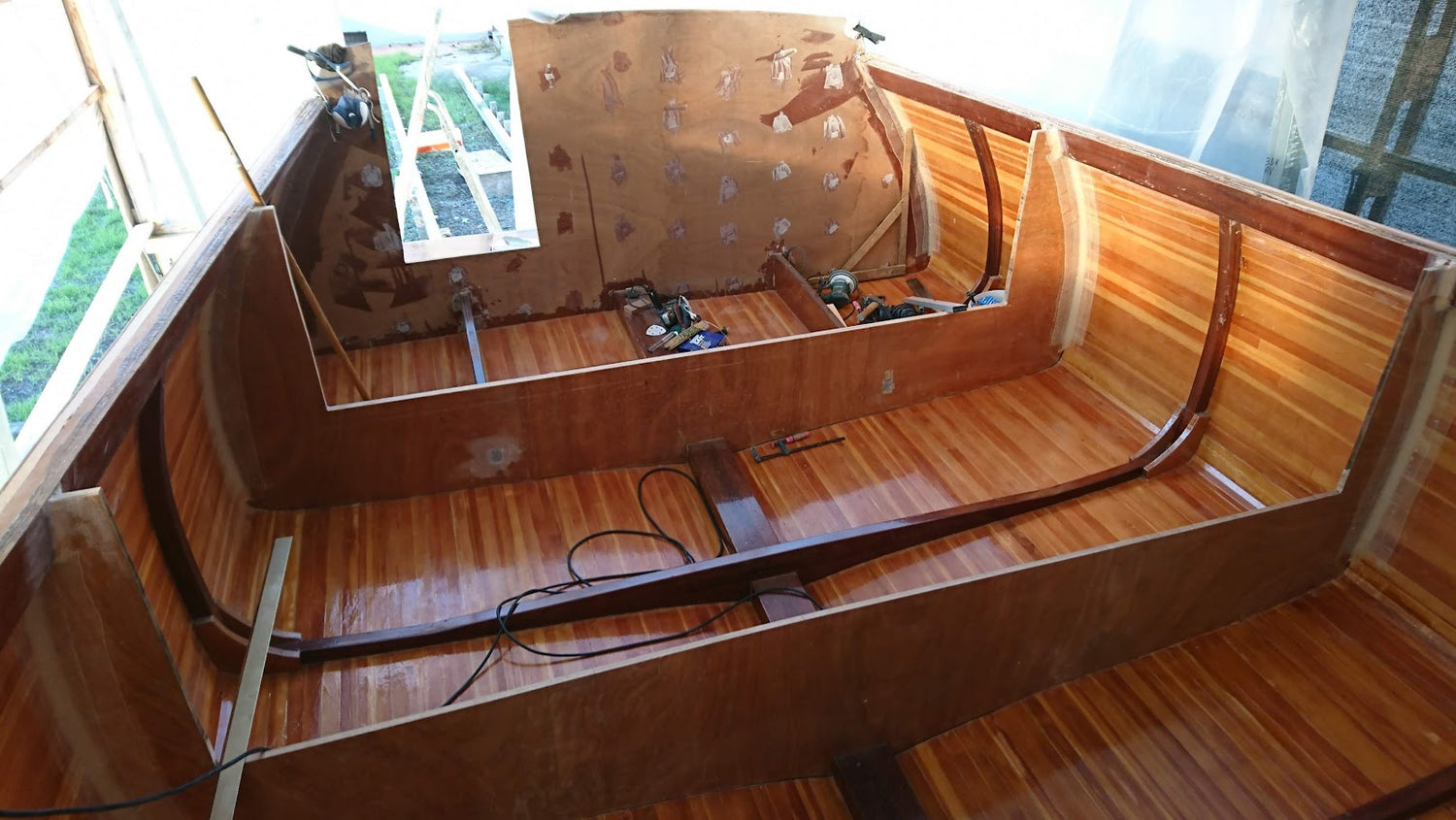

The wood
Advantages of wooden construction with modern techniques
- Greater stiffness
- Greater durability over time
- Ease of repair
- It does not require complex or technological equipment
- Aesthetic, sensorial and emotional aspect
- It does not require models or complex moulds, and is therefore easily customizable according to needs
- Economically competitive in one-off
- It largely uses renewable resources
- Handcrafted and unique product
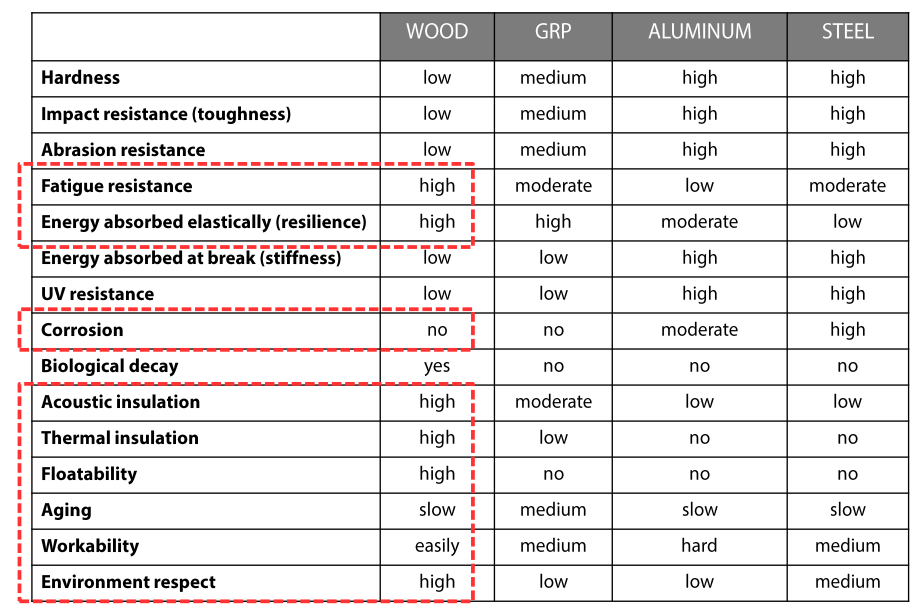
Qualitative differences between the various construction techniques
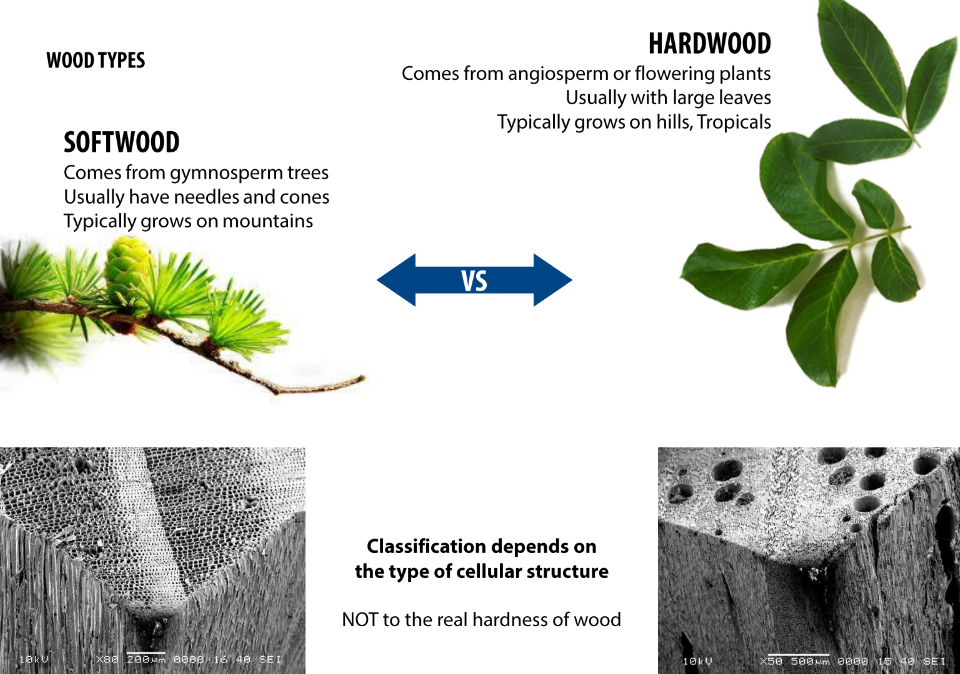
Wood classification
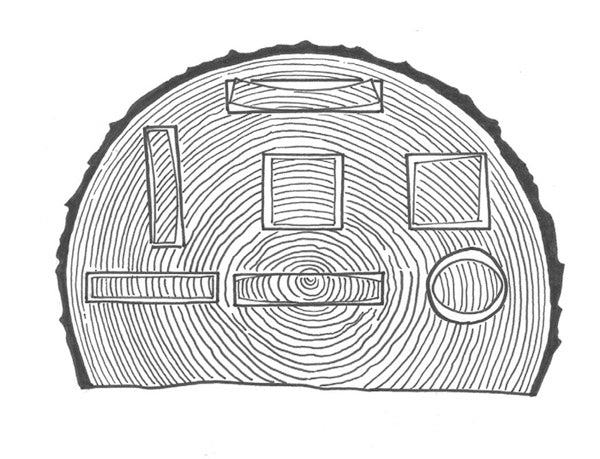
Wood deformation based on the type of cut
The image shows the typical deformations that wooden boards or strips undergo once cut. These deformations occur during the drying or natural seasoning of the wood after it is cut.
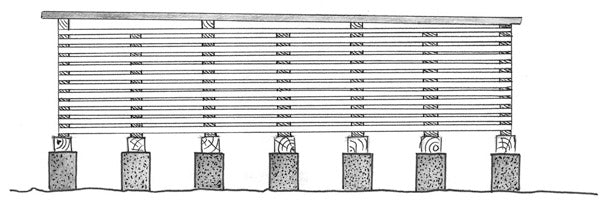
Seasoning and drying of wood
This diagram shows the typical arrangement of wooden planks during drying or seasoning to minimize warping. The boards must be stored in a sheltered place, raised from the ground, ventilated and possibly not exposed to changes in temperature and humidity.
The humidity of the wood in the freshly cut trunk can exceed 100% (water weight = fiber weight). Normal defined humidity value ~ 12%.
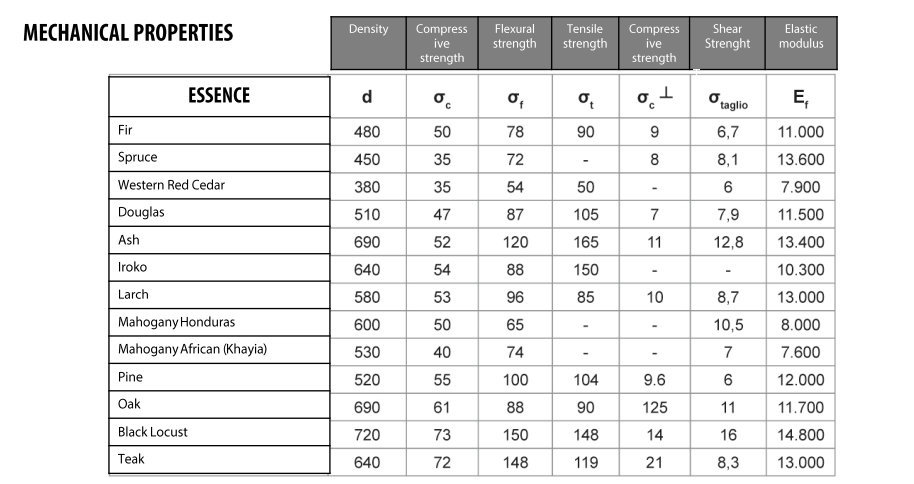
Mechanical characteristics
(1 N/mm2 = 1 MPa ≈ 0.1 kgf /mm2)
d : Density [kg/m3]
σc : Compressive strength in the direction parallel to the fiber [N/mm2]
σc ┴ : Compressive strength perpendicular to the fiber [N/mm2]
σf : Flexural strength [N/mm2]
σt : Tensile strength parallel to the fiber [N/mm2]
σshear : Shear resistance parallel to the fiber [N/mm2]
Ef : Flexural modulus of elasticity [N/mm2]
Note: the values provided are to be considered indicative as the characteristics can vary considerably from sample to sample.
Marine plywood
-

-
Main advantages of using marine plywood:
- Normalized material (UNI Directives)
- Stable material
- Remarkable multidirectional resistance
- It is possible to carry out numerical control cutting (CNC)
On the other hand: it allows you to create surfaces that can be developed flat and not double curved, it has a higher density than solid wood (density around 600kg/m3) with a consequent increase in the weight of the boat for the same thicknesses.
-
Typical marine plywood panels:
- Okumé Marine Plywood
- Mahogany Marine Plywood
RINA approved marine plywood panels are used for nautical construction.
The approval certifies the type of bonding (phenolic) of the various layers and the degree of resistance to water and boiling. -
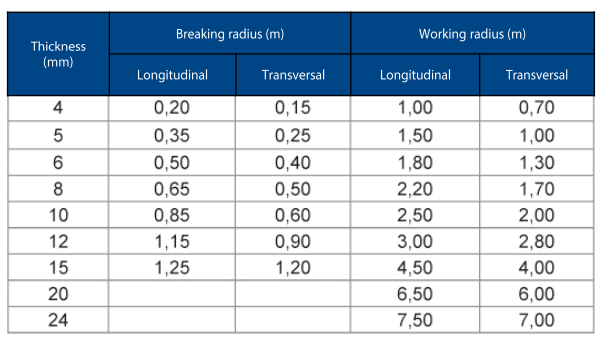
Curvature radii of the panels
Epoxy resin
-
Why is epoxy resin used?
- Allows structural bonding
- Excellent mechanical resistance, decidedly better than other resins
- Excellent waterproofness
- Practical to use, it is easily spread and laminated by hand
- Excellent absorption into the wood fibre
Characteristics of epoxy resin
Epoxy resin is in a liquid state and is made up of two elements:
Resin + Catalyst. -
Catalyzation phases
- After mixing you can apply it for about half an hour (depends on the room temperature)
- Over the next few hours it begins to harden, going from rubbery to hard.
- After about 24 hours it is already possible to work and sand it.
- After about 7 days it assumed its ideal mechanical characteristics.
Collapsible content
Practical attention
- Requires a precise mixing ratio as indicated on the packaging.
- It requires a temperature of use (especially in the 24 hours after installation) between 15°C and 30°C.
- Catalyzation heats the mixture based on the mass of product. Do not prepare large quantities in one go.
DIY thickeners
An excellent additive that is often available on construction sites is wood dust (or wood flour), the fine dust that remains in the sander's suction bags.
In addition to costing nothing, it has the advantage of having the right color to be used on wooden boats where the grouting remains visible. Talc can be used, although it has a tendency to absorb moisture. Additives such as sawdust or sand are not recommended
Structural thickeners
In case of structural applications we recommend using specific products:
- GLASS MICROFIBERS: are suitable for structural bonding
- MICROSPHERES: ideal for grouting or filling small concavities
- PHENOLIC MICROSPHERES: like the previous ones, but burnt brown in color. Easily sandable.
- COLLOIDAL SILICA: to produce grouts that are easily spreadable and do not leak

Epoxy manuals
We would like to point out two practical manuals (downloadable in PDF) written by West System and Cecchi on the use of epoxy resin with many of the construction or repair phases on boats described:

